Transactions, trust and tokens – Blockchain for healthcare
Blockchain is a hot topic everywhere, but especially in healthcare. Many experts say that it will have huge impact on health systems. For Dr Eberhard Scheuer, Chairman of the Health Information Traceability Foundation, blockchain holds big potential for sharing clinical data: “A central pillar of blockchain is trust, because data cannot be altered.”
Blockchain is an inherently complex technology. It’s a “digital ledger where transactions are stored and can be viewed and checked. Each new block in the chain contains new transactions to be stored and the hash of the previous block. They are immutable, distributed and have no central authority,” Scheuer described the technology. They can either be public like the Bitcoin blockchain or only available for registered participants in the case of permission-based blockchains.
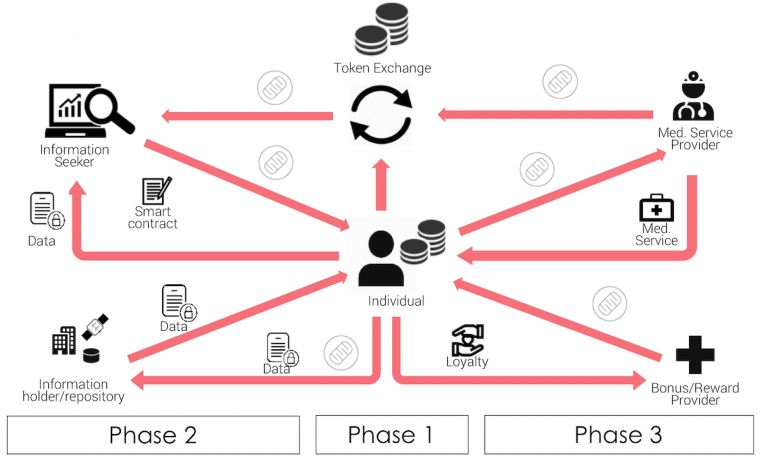
Phase1: Individuals are interested in earning tokens. In order to do so they must be willing to digitize their health-related data and make them shareable
Phase 2: Information seekers must acquire tokens in order to compensate individuals for giving access to their data – Existing data holders can enrich their data or earn tokens by making data accessable.
Phase 3: Tokens can be used to redeem Services – Tokens can be used in Loyalty programs.
Usability
In general, the technology is currently used to storage digital data and for so called smart contracts. The latter sets ground rules for the way transactions take place. They execute the contracts while monitoring compliance and automatically validate the results of each transaction. “And of course there are the cryptocurrencies or so called tokens. They are an essential part of public blockchains where it is used for rewarding the ones who are running nodes (e.g. miners) or are used to tokenize assets,” Scheuer added.
In the healthcare systems, the technology has not many practical applications as of yet. “We are still at the beginning. To date there are no applications that run fully on blockchain. Some applications use blockchains to store certain transaction data, some use it to call up registries or to control identities or access to applications.”
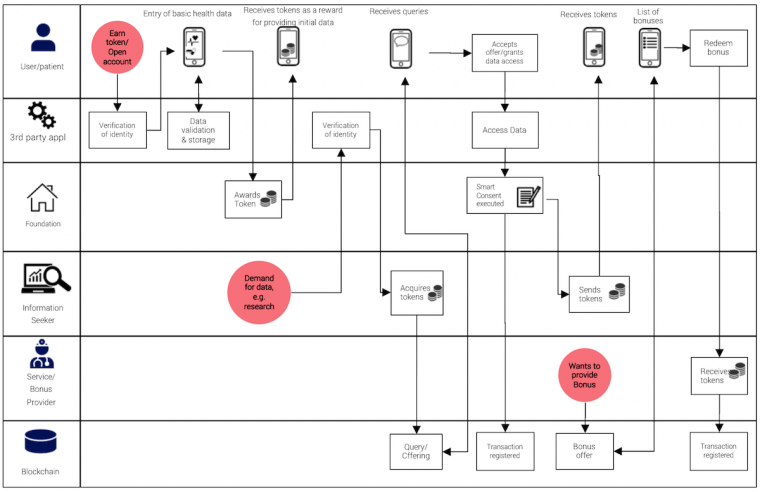
The HIT aligns network participants to achieve common goals — the growth of the network and the appreciation of the HIT token. Based on smart contracts the user/patient can receive tokens corresponding to the “value” of the data that is assigned by the information seeker. The smart contract that is incorporated in the request determines the access to the data and the transfer of token under the agreed conditions.
Opportunities
For Scheuer, there are several ways how the technology could benefit the healthcare systems. Firstly, it could increase trust in the digital applications in a hospital. For example by securing that nobody can temper with the data a connected insulin pump uses to calculate the dosage. “Moreover, smart contracts can be used to optimize and automate certain processes in the healthcare system.”
Secondly, using the crypto-tokens a reward system could be built. That way the one who does the work, actually gets the benefit from it. “I personally think that the ability to incentivize network participants with tokens is the most important aspect of blockchains.”
Thirdly, it provides the patients with a secure way to control and access their personal data. “If access to data can be rewarded and controlled by the individual this opens up a treasure of data which everybody in healthcare is hunting for. If data is not buried in silos this will indeed improve the basis for better diagnosis and treatments.”
Although, those are all benefits for the healthcare system, Scheuer urges cautions: “We should not believe that blockchain can solve the persisting problems of healthcare like the lack of technical and semantic interoperability. Usability of blockchain still needs much improvement.”
